Eliminate Waste and Streamline Project Execution
1. What is Lean Startup?
Lean startup is a method that aims to create the basic form of a product or service with minimal cost and time, and then quickly grow the product based on customer feedback. This method is widely recognized as a strategy for reducing “waste” caused by assumptions and creating what customers truly want.
To be successful, you don’t just have to create a product with passion, you have to have a deep understanding of real customer needs and respond in the right way. Lean Startup is a strategy to avoid mere complacency, and is also said to be a “next generation management method” that supports the development of new businesses.
Lean Startup Background
American entrepreneur Eric Ries introduced the concept of Lean Startup based on his own startup experience. His ideas have had a huge impact on the business world, and many companies and individuals still use them today. He shares his experience and knowledge on his blog “Startup Lessons” and has provided product strategy advice to many companies.
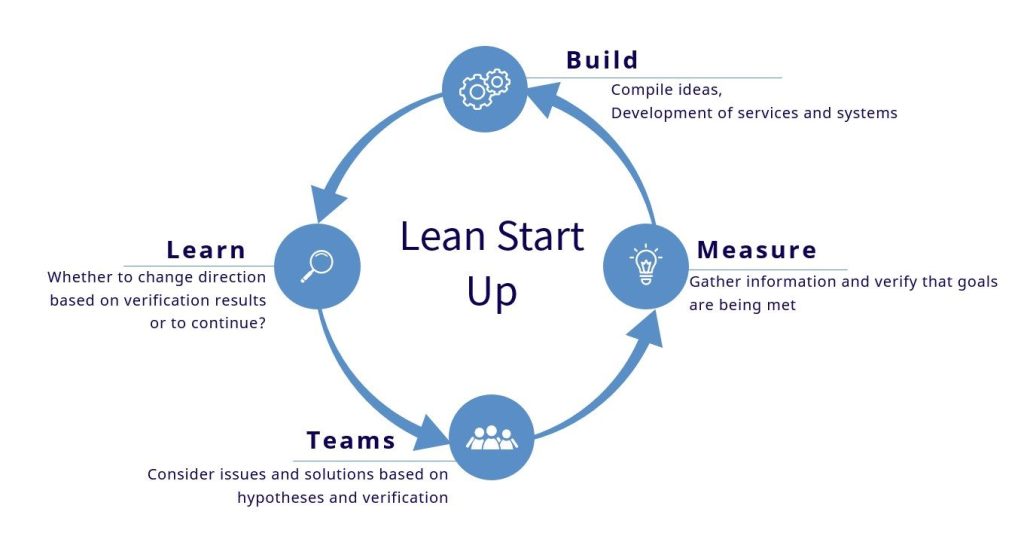
2. Basic process of Lean Startup
1. Hypothesis Setting
The first step is to formulate a hypothesis about your business idea. This hypothesis is based on customer needs and market trends.
2. Create a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
An MVP is the simplest version of a product or service for validating new ideas. At this stage, you create a product with minimal functionality and bring it to market.
3. Measure and Learn
After you bring your MVP to market, collect customer reactions and feedback and use that information to improve your product. This feedback loop repeats until the product is perfect.
4. Pivot or Continue
If the hypothesis is incorrect as a result of measurement and learning, a decision is made whether to change the direction of the strategy (pivot) or continue the current direction.
3. How to Incorporate Lean Startup in System Development Projects
3.1 Hypothesis Setting
Through the process of design thinking, we develop hypotheses to clarify what value a new system or feature will provide to users and the business.
3.2 Confirmation using Prototypes and Documents
Developing a system and then verifying it is already wasting a lot of time and effort. First, we create a product that is sufficient for confirmation and conversation with users, and then we repeatedly conduct interviews with users to verify whether sufficient effects can be obtained based on the product.
Specifically, we check the validity of the hypothesis based on prototypes (wireframes and mockups) and documents. Based on these deliverables, we will conduct feedback sessions with users and stakeholders to confirm the direction of the system.
3.3 Iterative Documentation Updates and Prototyping
Based on the feedback, update your hypothesis and re-prototype. By repeating this cycle, we gradually narrow down the requirements and direction of the system before moving on to actual development.
3.4 Transition to Actual Development
After sufficient confirmation and feedback, we will move on to actual system development. At this time, we will incorporate agile methods and other methods to complete the system by repeating releases and feedback in short cycles.